Create Your First Project
Start adding your projects to your portfolio. Click on "Manage Projects" to get started
Gait Analysis, Femur MRI Analysis, and Femur Implant Design
Project type
Biomedical Engineering, Mechanical Design
Date
Dec 2021 - Feb 2022
Skills
Slicer · SOLIDWORKS · Meshmixer
This biomedical engineering project involved three distinct phases, each building upon the previous to ultimately design and test a femur implant.
Phase 1: Gait Analysis
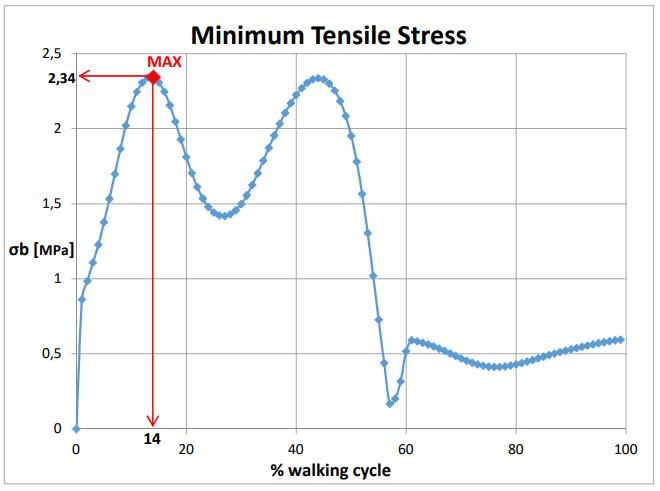
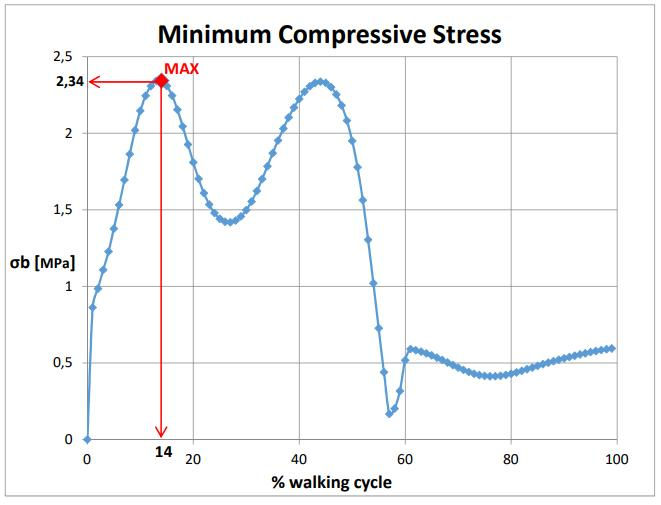
The first phase focused on analyzing gait data to understand the forces exerted on the femur during walking. Using real-life measurements from a gait analysis study, the project assessed the ground reaction forces and 3D joint forces at the ankle, knee, and hip. The analysis provided crucial insights into the load distribution on the femur during different stages of the gait cycle, which served as the foundation for the subsequent phases of the project.
Phase 2: Femur MRI Analysis and 3D Modeling
In the second phase, MRI scans of the femur were processed using 3D Slicer and Meshmixer software to create a precise 3D model of the femur. This model was then smoothed and refined to ensure accuracy for further analysis. This 3D model provided geometric data that would be used in the design of the femur implant. The model also allowed for a visual inspection of the femur structure, helping to identify areas of interest for implant placement and load-bearing analysis.
Phase 3: Femur Implant Design and Load Testing
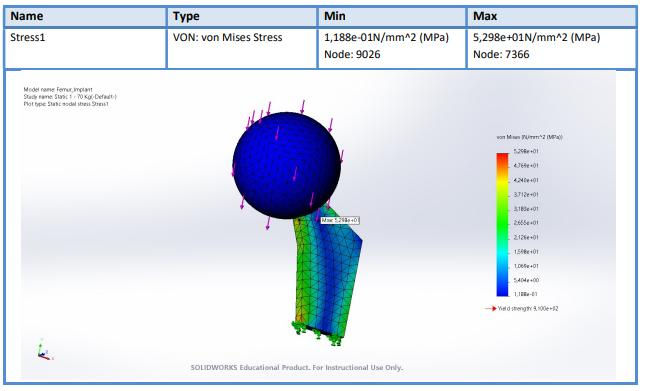
The final phase involved designing a femur implant using the 3D model generated in Phase 2. The implant was modeled with key dimensions derived from the femur geometry. Titanium Ti-8Al-1Mo-1V was selected as the material for the implant due to its superior mechanical properties. The implant underwent static load testing under three different load conditions (70 kg, 150 kg, and 300 kg) to evaluate its performance and identify critical stress areas. The analysis showed that the implant could withstand the applied loads without exceeding the material's yield strength, indicating a successful design. The maximum stress and displacement values were recorded, with critical areas identified for further optimization.